Cloud Computing : Why is it Revolutionizing Software Development?

Cloud computing refers to the computing services, including - servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, or intelligence — over the Internet (or the Cloud).
Cloud computing has become the backbone of modern IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to innovate and scale efficiently.
For simplicity, transitioning to the cloud is akin to using a taxi service. Instead of purchasing and maintaining an expensive car, you have the flexibility to choose the model of taxi that suits your immediate needs at a fraction of the cost. Similarly, the cloud provides a range of services—from compute power to advanced analytics—tailored to your unique requirements, all while keeping operational complexity to a minimum.
Traditional IT vs. Cloud Computing
Traditionally, software development involved significant upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and data centers. This "on-premises" approach required substantial capital expenditure, ongoing maintenance, and dedicated IT staff to manage the infrastructure.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, provides a pay-as-you-go model. You rent computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, from cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This eliminates the need for significant upfront investments and allows you to scale your resources up or down based on demand. You can operate all your workloads with best-of-the-breed security services, monitoring services and overall a much higher operational experience.
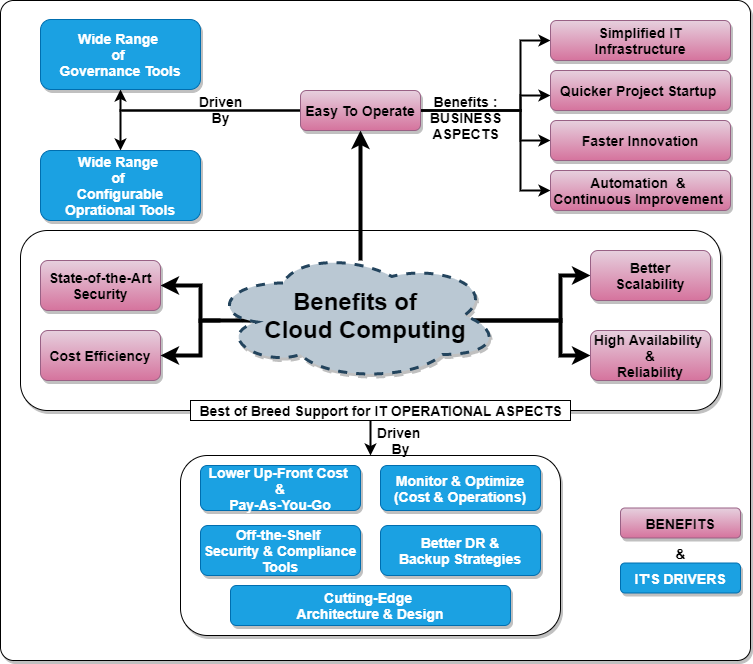
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
The benefits of cloud computing can be summarized using two broad aspects :
- The Benefits under the Business Aspects
- The Benefits under the IT Operational Aspects
Business Aspects :
With a wide range of governance tools and easy to configurable operational tools, cloud computing greatly simplifies our IT infrastructure which results into following direct benefits :
- Simplified IT infrastructure: The ease of operation in the cloud computing environment allows the business to focus more on it's business and less on it's IT operational complexities.
- Quicker Starup Time: With simplified infrastructure, getting started on a new project becomes lot quicker compared to traditional environments. It reduces the time and complexities in provisioning servers, setting up the secured environments, replicating environments and so on; all using simpler and configurable tools.
- Faster Innovation: The cloud computing also, help us innovate faster making the latest tools & technologies readily available for use. For example, AWS provides solutions like AWS EMR, AWS SageMaker where we can easily setup complex bigdata or analytics environments using few simple guided configurations. We can even get many industry specific data for our research form it's data marketplace(AWS Data Exchange). Utilize an array of choices in the analytic and vizualiztion tools, to meet the needs of our business analysts or development teams.
- Faster Time to Market: Simpler IT infrastructure, enhances our productivity and improves the time-to-market for our newer products or features, providing a significant advantage in the ever competitive market-place.
- Automation & Continuous Improvement: Better visibility and easy configurable aspect enables us to identify and automate our repetitive processes. Thereby, helping us in our goal towards improved automation and continuous enhancement.
IT Operational Aspects:
The cloud computing environments provide the best of the breed support for our key IT operational aspects such as:
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Reduced Capital Expenditure (CapEx): No need to invest heavily in hardware and infrastructure.
- Pay-as-you-go Model: Only pay for the resources you consume, optimizing costs.
- Economies of Scale: Cloud providers leverage their massive scale to offer competitive pricing.
- Scalability and Agility:
- Rapid Scaling: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak loads.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Quickly deploy applications and services, accelerating development cycles.
- Increased Agility: Adapt to changing business needs and market demands with greater flexibility.
- Enhanced Security, Reliability and Availability:
- High Availability: Cloud providers maintain redundant infrastructure to ensure minimal downtime.
- Disaster Recovery: Built-in disaster recovery mechanisms to protect data and applications from outages.
- Improved Security: Robust security measures and compliance certifications to safeguard your data.
Real-World Examples
- E-commerce: Cloud computing enables e-commerce platforms to handle sudden traffic surges during peak shopping seasons, ensuring a seamless customer experience.
- FinTech: Financial institutions leverage cloud-based services for secure and scalable data processing, fraud detection, and personalized customer experiences.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers use cloud platforms to store and analyze patient data, facilitate telemedicine, and improve medical research.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is no longer a futuristic concept; it's the foundation of modern software development.
Just as taxi services revolutionized personal transportation, cloud computing is transforming the way we build, deploy, and scale software applications. By understanding the core principles and leveraging the power of the cloud, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, innovation, and success.