Cloud Migration: 5 Key Steps for a Successful Journey
Migrating to the cloud is no longer just an IT initiative; it's a strategic move to unlock operational efficiency and drive business transformation. The primary objective behind a cloud migration journey is to harness the benefits of scalability, cost-efficiency, robust security, and compliance. Beyond operations, the cloud empowers businesses with faster time-to-market, agile change management, and the ability to innovate and roll out products more rapidly.
The Journey is not Without it's Challenges
However, this transformative journey is not without its challenges. Depending on the size and complexity of your system, a cloud migration can take anywhere from a few weeks to over a year. New environments, skill gaps, and the inherent complexities of hybrid or multi-cloud setups can introduce significant risks.
Without a well-thought-out strategy, these risks can manifest as unforeseen cost escalations, security breaches, compliance violations, and costly rework due to ill-planned cloud services. Hybrid or multi-cloud environments add further layers of complexity, making the risks of rework and inefficiency even more pronounced.
The Need for a Robust Strategic Plan

A robust strategic plan is the cornerstone of a successful cloud migration. Such a plan not only mitigates risks but also ensures a smoother, more effective journey. This is where frameworks like AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF) and Migration Acceleration Program (MAP) come in very useful.
- AWS CAF emphasizes six critical dimensions—business, process, people, platform, operations, and security—to guide a comprehensive migration strategy.
- AWS MAP offers tailored training, partner expertise, and a phased approach (Assess, Mobilize, Migrate & Modernize) that reduces risk, automates processes, and accelerates the migration journey.
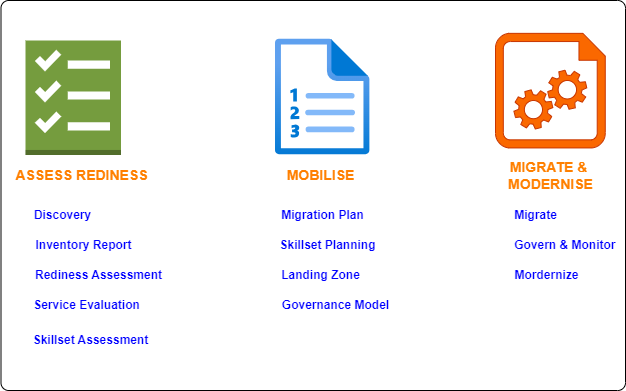
In this blog post, we’ll break down the insights from CAF and MAP into five key steps to ensure a smooth and effective cloud migration journey planned for continuous improvement. Even though we would be discussing using AWS specific guideline, tools and frameworks, the approach will more or less hold true for any other clould migration programs.
5 Key Steps for a Successful Journey
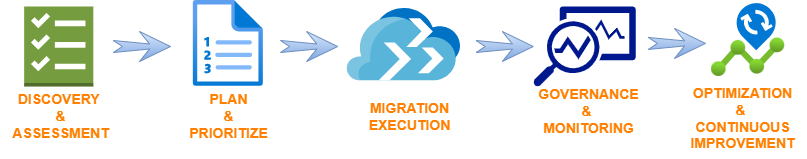
Step 1: Discovery & Assessment
A successful cloud migration begins with a deep understanding of your current systems and their readiness for the cloud.
1.1 Discovery
The discovery process is all about gaining a complete view of your IT landscape. Tools like AWS Application Discovery Service and AWS Migration Hub can help automate the process of creating an inventory and categorizing applications for planning purposes.
- Application Inventory: Collect detailed information about each application, including: Name, type (web, mobile, batch, database), dependencies and criticality (business impact), technology stack and size, deployment frequency.
- Application Categorization: Organize applications into groups for migration prioritization:
- Criticality: Tier 1 (mission-critical), Tier 2 (important), Tier 3 (less critical)
- Complexity: Simple (standalone), Complex (with many dependencies)
- Cloud Suitability: Cloud-native, Cloud-ready, Re-platforming required, Re-architecting required
1.2 Cloud Readiness Assessment
Evaluate the technical and business readiness of your applications to understand potential challenges and impacts.
- Technical Readiness:
- Map dependencies, conduct security assessments, and evaluate compliance requirements.
- Assess infrastructure, OS, software, and licensing compatibility with AWS.
- Business Readiness:
- Assess downtime tolerance, cost implications, and change management needs.
- Plan for necessary training to upskill teams.
1.3 AWS Services Evaluation
Use this stage to align your applications with the right AWS services and frameworks to optimize your migration.
-
Service Selection: Match workloads to appropriate AWS services such as Compute (EC2, ECS, EKS), Storage (S3, EBS, Glacier), Networking (VPC, Route 53), Databases (RDS, Aurora, DynamoDB) and Security (IAM, Security Groups, VPC Endpoints)
-
AWS Well-Architected Framework: Apply its five key pillars to ensure a robust architecture such as Operational Excellence, Security, Reliability, Performance Efficiency, and Cost Optimization
1.4 Assess Skillset & Plan Training
A successful cloud migration requires a skilled team that is prepared to handle the complexities of the new environment. Assessing the current skillset and addressing gaps through proper training is a critical part of the Discovery and Assessment phase.
This thorough discovery and assessment process creates a solid foundation for the next steps in your cloud migration journey. Assess Skillset & Plan Training
Step 2: Plan and Prioritize
Create a dependency map to understand the order of migration based on their dependency structure. Develop a Prioritization Matrix considering factors like Business value, complexity, risk, cost, dependencies, and time to market. Use these as input to create a phased approach for migration.
Migration Waves: Group applications into batches for migration.
- Pilot Phase: Start with a small set of low-risk, high-value applications to test the migration process and refine methodologies.
- Progressive Migration: Plan to gradually migrate applications in phases, starting with less critical applications.
- Choose your migration approach using standard migration strategies :
- Retire: Applications that are no longer needed.
- Retain: Applications that are not suitable for migration yet.
- Rehost: Applications to "lift and shift" as-is.
- Replatform: Minor changes for optimization on AWS.
- Refactor: Significant changes to modernize for the cloud.
Plan Governance Model: We need to plan the governance model and the landing zone in this phase. This will provide a centralized monitoring and governance for our migrated applications. We will discuss more on its usage and benefits in step-4.
Step 3: Migration Execution
Migration Execution is where your planning turns into action. Begin by executing Migration Waves, migrating applications in batches. Start with low-risk applications to test the process and scale up to critical systems as confidence builds.
AWS offers a variety of tools to simplify and automate the migration process:
- AWS Migration Hub: Centralized tool for orchestrating and tracking migrations.
- AWS Server Migration Service (SMS): Migrates on-premises servers to EC2.
- AWS Database Migration Service (DMS): Facilitates database migration to AWS.
- AWS Cloud Migration Factory: Coordinates and automates manual processes for large-scale migrations.
- AWS Mainframe Modernization: Helps modernize and migrate mainframe workloads.
- AWS Transfer Family: Supports seamless file migrations.
- AWS DataSync: Automates the transfer of large datasets to the cloud.
Key practices to streamline execution:
- Leverage Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with tools like AWS CloudFormation or Terraform to ensure clean, consistent resource provisioning and scaling.
- Validate migration outcomes after each wave to ensure data integrity, performance, and security.
- Incorporate automated testing and monitoring to quickly identify and resolve issues during execution.
A phased, tool-driven approach ensures a smooth transition while minimizing risks and disruptions to business operations.
Step 4: Governance and Monitoring
Governance and Monitoring play a crucial role in ensuring a structured, transparent, and accountable approach to cloud migration. They help organizations mitigate risks, align with business goals, and achieve operational excellence throughout the migration process.
By leveraging these tools and practices, you can centrally manage security guidelines, enforce compliance policies, monitor performance, track resource utilization, and safeguard data. Early adoption of governance and monitoring minimizes risks such as human errors, malicious actions, and unexpected cost overruns, paving the way for a smoother migration.
Key Practices and Tools:
- Multi-Account Management: Use AWS Control Tower to establish a robust account structure for managing costs, security, infrastructure, and policies across multiple accounts.
- Monitoring: Gain visibility into application health and activity using tools like AWS CloudWatch, X-Ray, and CloudTrail.
- Cost Management: Track and manage migration expenses effectively with AWS Cost Explorer and Budgets.
- Security Automation: Enhance security posture by automating compliance checks and threat detection using AWS Security Hub.
Implementing governance and monitoring practices early ensures better control, cost-efficiency, and security, reducing risks while accelerating cloud adoption success.
Step 5: Optimization & Continuous Improvement
Regularly review and refine the migration process based on lessons learned. Continuously refine the migration process by reviewing outcomes and leveraging insights from governance and monitoring tools to drive optimization. Regular evaluations ensure cost efficiency, performance, and security.
- Cost Optimization: Regularly analyze cloud expenses and identify improvements, such as using reserved instances, spot instances, or right-sizing resources.
- Performance Tuning: Monitor cloud application performance and fine-tune configurations as needed.
- Security Best Practices: Strengthen security with measures like IAM policies, security groups, encryption, and vulnerability scanning to safeguard resources.
Iterative improvement ensures long-term success and cloud operational excellence.
Conclusion
To navigate the complexities of a migration process, it's crucial to integrate a robust governance and monitoring framework early in the migration journey.
By implementing the right tools and processes, organizations can gain valuable insights into their systems and accelerate the learning curve. This proactive approach not only minimizes the risks associated with the migration itself but also lays a strong foundation for future enhancements, automation, and continuous improvement within the cloud environment.